Introduction
Understanding schizophrenia types and symptoms is crucial in recognizing and addressing this complex mental health condition. Schizophrenia is a chronic disorder that impacts how individuals think, feel, and perceive their surroundings. Each type of schizophrenia has unique features, but knowing the symptoms of all types is essential for early intervention and proper support.
In this guide, we explore the six main types of schizophrenia and their symptoms to provide a clearer understanding of this challenging disorder.
1. Paranoid Schizophrenia: Types and Symptoms
Paranoid schizophrenia is among the most recognizable schizophrenia types and symptoms. It is marked by:
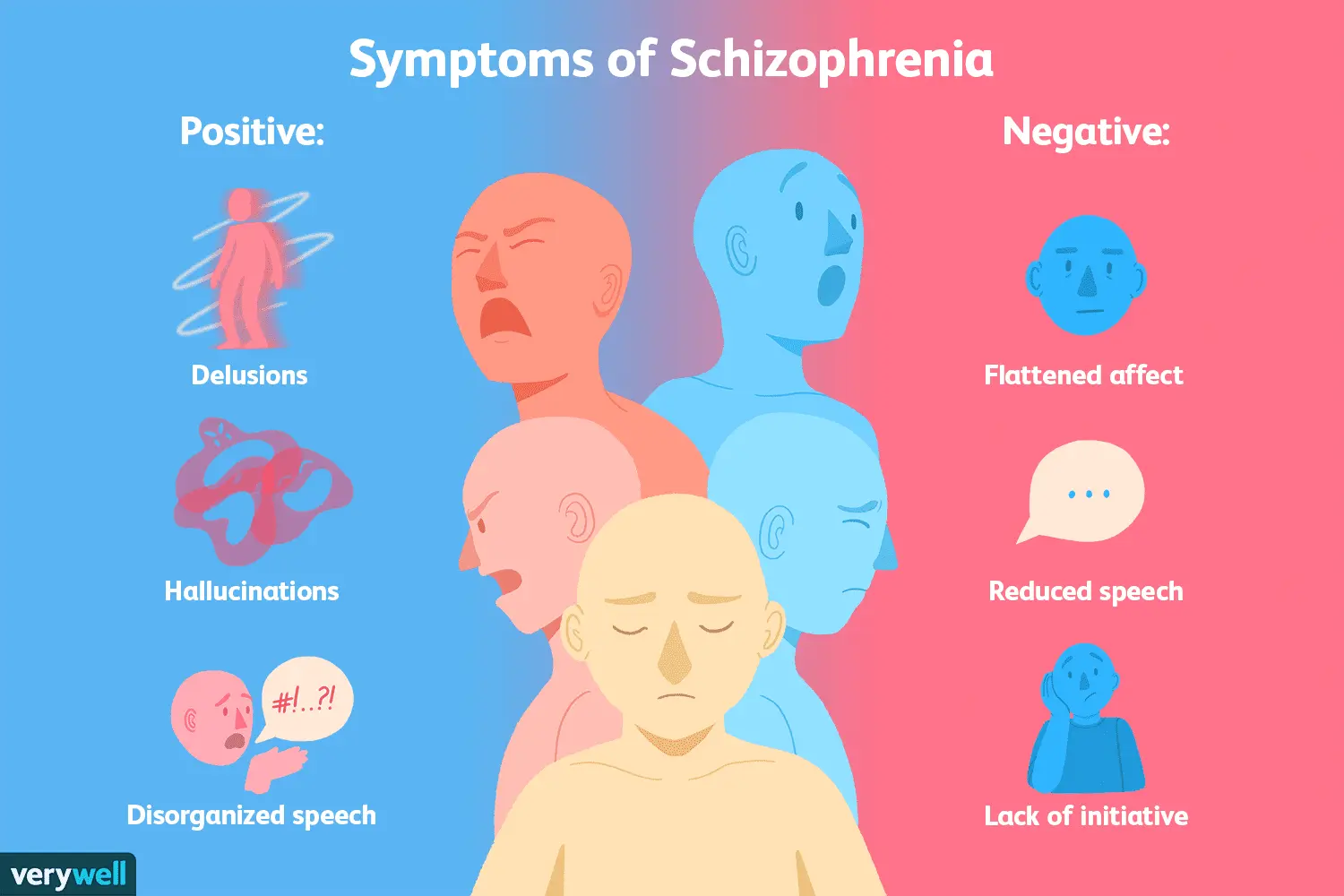
- Hallucinations: Hearing voices or seeing things that are not real.
- Delusions: Believing in scenarios that are not based in reality, such as feeling persecuted or being under threat.
Despite these symptoms, individuals with paranoid schizophrenia may still have clear thinking and functional cognitive abilities.
For Consultation with the Best Psychiatrist in Delhi for the Best Schizophrenia Treatment in Delhi, consider visiting:
2. Disorganized Schizophrenia: Types and Symptoms
Disorganized schizophrenia significantly impacts logical thinking and emotional expression. Key schizophrenia types and symptoms in this category include:
- Disorganized Speech: Difficulty forming logical sentences or conversations.
- Inappropriate Emotional Reactions: Expressing emotions that don’t align with the context.
- Erratic Behavior: Performing actions that seem irrational or unpredictable.
This type of schizophrenia often makes daily tasks challenging, requiring support for routine activities.
3. Catatonic Schizophrenia: Types and Symptoms
Catatonic schizophrenia is defined by movement disturbances. Common schizophrenia types and symptoms include:
- Catatonic Stupor: Periods of immobility or a lack of response to surroundings.
- Excessive Movement: Episodes of hyperactivity or repetitive motions.
- Echolalia and Echopraxia: Mimicking words or actions of others.
This form of schizophrenia requires immediate attention to prevent harm during episodes of immobility or agitation.

For more insights and support, refer to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
4. Residual Schizophrenia: Types and Symptoms
Residual schizophrenia refers to cases where the individual has experienced the active phases of schizophrenia in the past but currently exhibits mild symptoms. Common signs include:
- Mild Hallucinations or Delusions: These are less intense than during active phases.
- Social Withdrawal: A tendency to avoid social interactions.
- Lack of Motivation: Difficulty engaging in daily activities.
While the symptoms are less severe, ongoing care and support are essential.
5. Undifferentiated Schizophrenia: Types and Symptoms
When an individual’s symptoms do not fit neatly into one specific category, they are diagnosed with undifferentiated schizophrenia. This type may involve:
- A combination of hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized behavior.
- Overlapping features of multiple schizophrenia types and symptoms.
This diagnosis highlights the spectrum nature of schizophrenia.
For more insights and support, refer to World Health Organization (WHO)
6. Schizoaffective Disorder: Types and Symptoms
Schizoaffective disorder involves symptoms of schizophrenia combined with mood disorders such as depression or bipolar disorder. Symptoms include:
- Psychosis: Experiencing hallucinations or delusions.
- Mood Episodes: Periods of intense depression, mania, or both.
This type requires a comprehensive treatment approach addressing both psychotic and mood-related symptoms.
Common Symptoms Across All Types of Schizophrenia
While each type of schizophrenia presents distinct symptoms, some are common across all types, including:
- Cognitive Impairments: Difficulty concentrating or processing information.
- Negative Symptoms: Reduced emotional expression, social withdrawal, and lack of motivation.
- Behavioral Changes: Unpredictable actions or difficulty completing daily activities.
Understanding these shared symptoms is key to identifying schizophrenia early and seeking appropriate care.

How to Support Someone with Schizophrenia
Caring for someone with schizophrenia can be challenging, but your support can make a significant difference. Here’s how you can help:
- Encourage Professional Help: Seek guidance from mental health professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Provide Emotional Support: Listen to the individual’s experiences without judgment.
- Learn About Schizophrenia: Understanding the different schizophrenia types and symptoms can help you offer informed support. For more insights and support, refer to National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) .
Conclusion
Understanding schizophrenia types and symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and effective management. By recognizing the signs and seeking timely help, individuals with schizophrenia can lead fulfilling lives.
Raising awareness and reducing stigma surrounding schizophrenia can pave the way for a more supportive and inclusive society